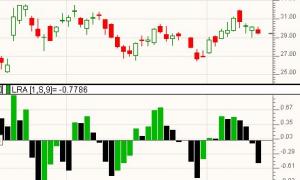
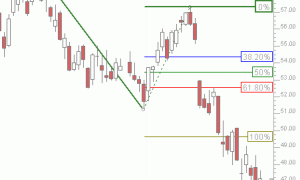
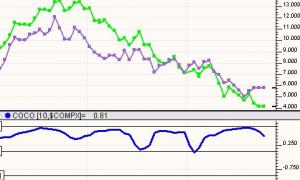
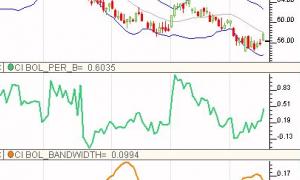
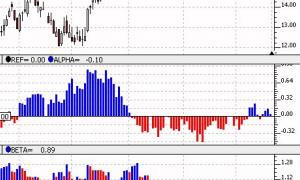
Linear Regression Acceleration
First, the data, based on the price selected, is smoothed using the moving average period and type. If you prefer no smoothing, choose a period of 1 here. The resulting data is then used to form regression lines ending at each bar, using the regression period specified. The linear regression acceleration of each bars regression line is then recorded as the change in slope of the regression line from the slope of the regression line of the previous bar. For instance, using the preferences specified above, the raw closing price would be used (smoothing period of 1).